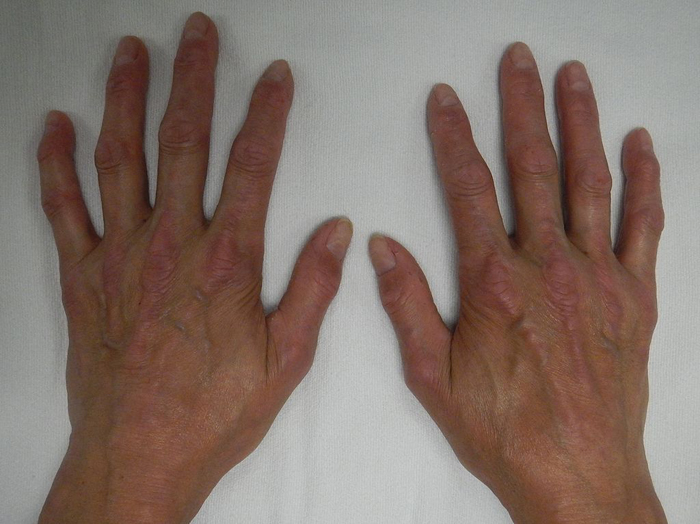
Crest Syndrome
Matlike telangiectasia, especially the face, upper trunk, and hands; also in the entire GI tract. Calcinosis over bony prominences, finger tips, elbows, and trochanteric regions.
The term CREST is an acronym derived from the five most prominent features:
- C – Calcinosis – calcium deposits in the subcutaneous layer of the skin
- R – Raynaud’s phenomenon – extreme sensitivity to cold or stress
- E – Esophageal dysfunction – swallowing problems caused by scarring
- S – Sclerodactyly – tightening of the skin confined to fingers and toes
- T – Telangiectasia – red spots on the hands, palms, forearms, face and lips
Causes of Crest Syndrome
Pathogenesis unknown. Primary event might be endothelial cell injury in blood vessels, the cause of which is unknown. Early in course, target organ edema occurs, followed by fibrosis; cutaneous capillaries are reduced in number; remainder dilate and proliferate, becoming visible telangiectasia. Fibrosis due to overproduction of collagen by fibroblasts.
Symptoms of Crest Syndrome
Crest syndrome is a subset of scleroderma, a disorder that leads to thickening, hardening and tightening of your skin and connective tissue. In localized scleroderma the damage is confined to your skin and the tissue just beneath it, but systemic scleroderma is more far-reaching, affecting blood vessels and internal organs as well.
Diagnosis
Clinical findings confirmed by dermatopathology. You may also have laboratory tests to look for antibodies that are frequently found in the blood of people with scleroderma, especially the anticentromere antibody, which occurs in most people with CREST. Yet even this isn’t definitive because not everyone with CREST has the antibodies.
Treatment
Symptomatic Systemic glucocorticoids may be of benefit for limited Periods early in the disease. All other systemic treatments (EDTA, aminocaproic acid, D-penicillamine, paraaminobenzoate, colchicine, immunosuppressive drugs) have not been shown to be of lasting benefit. Presently, interferon-γ is being tested clinically, as is photopheresis.
Telangiectasia. Dilated capillaries can be hidden with makeup or reduced or eliminated with laser therapy.
References