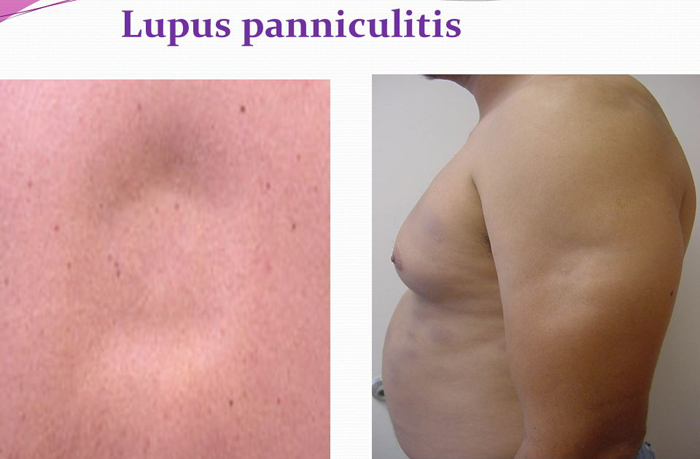
Chronic lupus panniculitis is a form of CCLE in which there are firm, circumscribed subcutaneous nodules on the face, scalp, breast, upper arms, thighs, and buttocks. Most but not all patients also have typical lesions of DLE. Usually a form of cutaneous lupus, but may occur in SLE.
Causes of Chronic Lupus Panniculitis
Patients with DLE probably have genetic predisposition; however, the precise genetic factors that increase the risk of this disease are unknown. The disease usually manifests following UV light exposure, but other triggers or inciting factors also must contribute.
Symptoms of Chronic Lupus Panniculitis
The symptoms of lupus vary and people who suffer from the disease rarely have the same symptoms. The specific symptoms of lupus are also experienced at different intensities by people with the disease.
General symptoms of lupus are: joint pain, swelling and sensations of burning; rashes on the face, neck or scalp; increased sensitivity to sunlight; scaling of the skin on the body regions exposed to the sun; inflammation and soreness of the mouth and nose.
Treatment
- The goals of management are to improve the patient’s appearance, to control existing lesions and limit scarring, and to prevent the development of further lesions.
- Sun protection. Stay indoors whenever possible between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. Cover up – wear a broad brimmed hat, long sleeves, high collar, long trousers or skirt, socks and shoes.
- Corticosteroid injections may be used for small lesions.
- Oral steroids. Systemic steroid medicines are usually not necessary except in severe DLE. They may be continued for a few months, or several years. Steroids have important side effects, so discuss these with your dermatologist.
- Cosmetic camouflage may be used to disguise unsightly plaques.
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors have also been used recently in patients with cutaneous lesions of LE. In addition, topical retinoids have been reported to be helpful. Lastly, topical imiquimod has been reported to be effective in one patient.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2856385/
- https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/lupus-erythematosus-panniculitis